As an Amazon Associate, Modded gets commissions for purchases made through links in this post.
Have you tried to buy a new car in the last two years? There isn’t enough room on the price tag to fit all the numbers. Prices have soared for cars, trucks, SUVs and more. So, what gives? What’s happened to the auto industry supply chain to cause these problems?
We’re living in precarious times. Numerous factors have collided to make many cars unaffordable for the average consumer. Here are seven reasons why the automobile industry supply chain has struggled and will continue to feel pain.
1. Chip Shortage
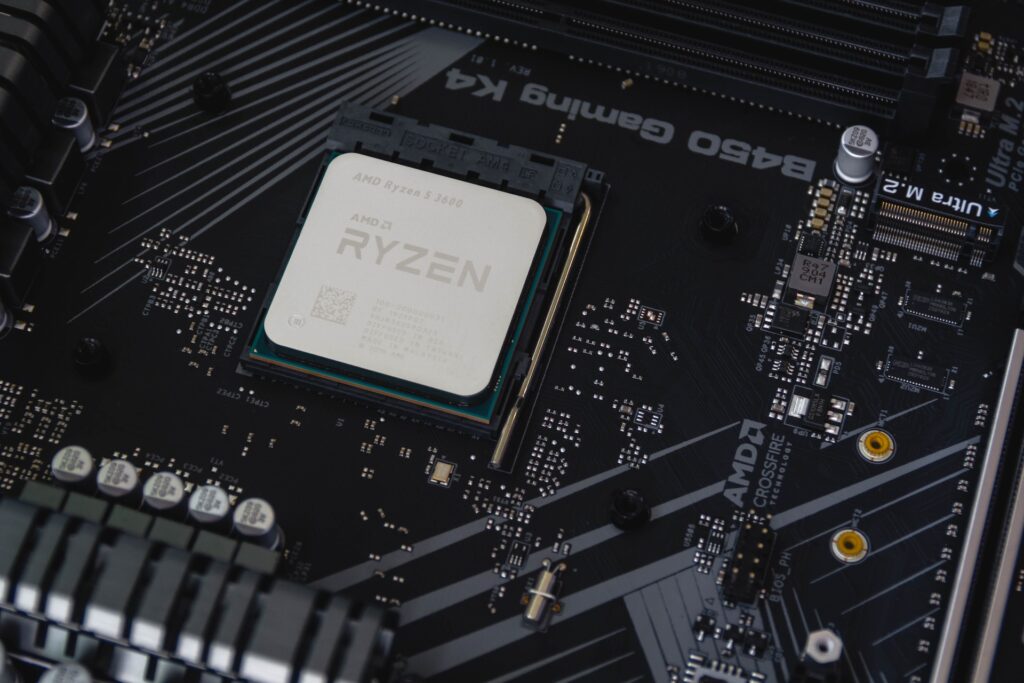

The chip shortage is one of the top reasons for the supply chain pain. The chips, or semiconductors, act as the computer of a car. These tiny chips help your car with numerous factors, including data transmission through telematics and infotainment devices. Do you like listening to podcasts on the way to work? You can thank the semiconductors.
Semiconductors are critical technological devices, but there has been a massive shortage. In early 2020, many technology companies slowed production because of the pandemic. Without the chips, automakers couldn’t produce as many chips. Hope is on the horizon with federal legislation. In August 2022, President Biden signed the CHIPS and Science Act, providing nearly $40 billion in funding for semiconductors.
2. Trade Wars
The high car prices also derive from trade wars. In the last five years, the trade war between the U.S. and China has escalated, with both sides raising tariffs on particular goods like semiconductors. The U.S. also banned American companies from buying chips from certain Chinese manufacturers. These businesses had to turn to factories in Taiwan and elsewhere for chips, increasing demand and lowering supply.
3. Overseas Conflict
A trade war is only the tip of the iceberg for overseas conflict. The Russian invasion of Ukraine has also negatively impacted the automotive industry supply chain. In late February 2022, Russia launched attacks on the capital, Kyiv, and other cities. An overseas conflict 5,000 miles away might not seem important, but its ramifications quickly spread worldwide.
Russia is a massive country. In fact, its square mileage doubles second-place Canada. Many automakers have car production in Russia that halted. For example, Nissan paused production in Russia in March 2022 because of the invasion. Other automakers like Lexus said they wouldn’t sell cars in Ukraine in protest.
The invasion has also had ramifications for the chip shortage and other parts. For example, wire harnesses are vital pieces for auto manufacturing. In 2022, Mercedes-Benz said it had to reduce vehicle production because it faced a shortage of wire harnesses. If we’ve learned anything from 2022, the word shortage comes up often.
4. Raw Material Shortage

Building a car requires many parts sourced worldwide. You need steel, magnesium, copper, rubber, glass and other materials. One missing link in the chain causes significant disruptions and slower production time. Since 2022, most of the materials required for manufacturing have faced shortages. Experts foresee the raw material shortage to last into 2025, 2026 and beyond.
For example, look at steel. The Man of Steel himself, Superman, can’t help what we’re going through right now. The steel industry has suffered from lower inventory and extended lead times due to supply chain disruptions and factory closures. A survey of steel industry experts reveals 94% of professionals expect higher steel prices amid the struggles.
5. Pandemic Cultural Shifts
Think back to the spring of 2020 when the pandemic began. Did you start working from home? How often did you leave your house? Many people focused more on their mask design than the car they wanted to buy. Remote work came during the pandemic and stayed, heavily altering consumer priorities. Why would they buy a new car if they could stay home, order groceries and have entertainment in the living room?
The pandemic also caused shifts in manufacturing processes. Many cities and countries instituted regulations on indoor facilities, capping the number of inhabitants. Auto manufacturing happens indoors so that directly impacts the auto industry supply chain. Some countries like China shut down production entirely due to stay-at-home orders, straining the auto industry severely.
6. Fluctuating Demand
In 2020, demand sank for cars. In response, many automakers reduced vehicle production. This infamous year saw many people nationwide stay at home to avoid contracting the COVID-19 virus. However, in 2021, the first round of vaccines arrived from Pfizer, Moderna and others. The vaccines slowly opened the U.S. and other countries worldwide. Why does it matter? Vehicle production spiked ahead of expectations.
In 2021 and 2022, people started to get out more and wanted to compensate for feeling locked up in 2020. You may have taken a road trip or flown to tropical islands to escape it all. Many Americans moved or wanted a new car, splurging despite the high prices. Research shows vehicle sales will grow by 5.1% in 2023 and 3.3% in 2024.
7. Climate Change

A lot of our problems can go back to climate change. Rising ocean temperatures, extreme weather events and coastal erosion. How do they tie into the auto industry supply chain?
First, look at semiconductor production. Climate change has caused Taiwan’s worst drought in decades. The drought has led to a shortage of clean water required to clean the chip factories. A water shortage compromises the supply chain for cars, cell phones, washing machines and other appliances.
At home, severe weather has also affected domestic manufacturers. In early 2021, Texas faced a massive snowstorm, forcing Samsung and Infineon plants to close. The facilities lost power and the capacity to create semiconductors. How badly did it affect the auto industry supply chain? The one snowstorm caused months’ worth of damage, further putting the U.S. in the hole when it faced a semiconductor shortage.
Navigating the Auto Industry Supply Chain Pains
There are nearly 1.5 billion cars worldwide, so managing the automotive industry is hard, to say the least. The past three years have seen mighty struggles with auto manufacturing and other sectors. Supply chain disruptions have made car prices soar due to low supply. What has caused the troubles? These seven problems are directly related to supply chain pains.
Stay up to date with the latest by subscribing to Modded Minute.
Author
Jack Shaw is a senior writer at Modded. Jack is an avid enthusiast for keeping up with personal health and enjoying nature. He has over five years of experience writing in the men's lifestyle niche, and has written extensively on topics of fitness, exploring the outdoors and men's interests. His writings have been featured in SportsEd TV, Love Inc., and Offroad Xtreme among many more publications.